Philippines Government Structure
Free Shipping on US orders over $49 USD and 5 lbs or less at eVitamins.com!

 http://www.cannabis-seeds-store.co.uk/redebose.html
http://www.cannabis-seeds-store.co.uk/redebose.html
Government of the Philippines
Jump to navigationJump to search
| Judicial branch | |
|---|---|
| Executive branch | |
| Legislative branch | |
| Pamahalaan ng Pilipinas | |
 | |
| Jurisdiction | Philippines |
| Website | www |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Meeting place | Batasang Pambansa Complex (House of Representatives/Lower Chamber) GSIS Building (Senate/Upper Chamber) |
| Leader | President |
| Appointer | Election by popular vote |
| Headquarters | Malacañang Palace |
| Main organ | Cabinet |
| Departments | Executive departments of the Philippines |
| Court | Supreme Court |
| Seat | Manila |
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of the Philippines |
|---|
 |
Constitutional commissions[show] |
The government of the Philippines (Filipino: pamahalaan ng Pilipinas) is the national government of the Philippines. It is governed as a unitary state under a presidential representative and democratic and a constitutional republic where the President functions as both the head of state and the head of government of the country within a pluriform multi-party system.
The government has three interdependent branches: the legislative branch, the executive branch, and the judicial branch. The powers of the branches are vested by the Constitution of the Philippines in the following: Legislative power is vested in the two-chamber Congress of the Philippines—the Senate is the upper chamber and the House of Representatives is the lower chamber.[1]
Executive power is exercised by the government under the leadership of the President. Judicial power is vested in the courts with the Supreme Court of the Philippines as the highest judicial body.
Contents
- 1Legislative power
- 2Executive power
- 3Judicial power
- 4Constitutional commissions
- 5Office of the Ombudsman
- 6Local government
- 7See also
- 8References
Legislative power[edit]
The legislative power is vested in the Congress of the Philippines which consists of the Senate of the Philippines and the House of Representatives. The upper house is located in Pasay City, while the lower house is located in Quezon City. Both are in Metro Manila. The district and sectoral representatives are elected for a term of three years. They can be re-elected but they may not run for a fourth consecutive term.
Senators are elected to a term of six years. They can be re-elected but may not run for a third consecutive term. The House of Representatives may opt to pass for a vacancy of a legislative seat, which leads to a special election. The winner of the special election will serve the unfinished term of the previous district representative, and will be considered as one elective term. The same rule also applies in the Senate, however it only applies if the seat was vacated before a regular legislative election.
The current President of the Senate is Vicente Sotto, III, while the current Speaker of the House of Representatives is Alan Peter Cayetano.
Legislative power:
National government
- Senate
- House of Representatives
Local government
- Sangguniang Panlalawigan
- Regional Legislative Assembly
- Sangguniang Panlungsod
- Sangguniang Bayan
- Sangguniang Barangay
Executive power[edit]
The highest official is elected separately from the President by popular vote. The Vice President is first in line to succession if the President resigns, is impeached or dies. The Vice President is usually, though not always, a member of the president's cabinet. If there is a vacancy in the position of vice-president, the President will appoint any member of Congress (usually a party member) as the new Vice President. The appointment must then be validated by a three-fourths vote of the Congress.[2]
Executive leadership:
National government
- President
- Vice-President
- Cabinet Secretaries
Local government
- Provincial/Regional Governor
- Provincial/Regional Vice-Governor
- City/Municipal Mayor
- City/Municipal Vice-Mayor
- Barangay Captain/Barangay chairman
Judicial power[edit]
The judicial power is vested in the Supreme Court of the Philippines and lower courts established by law. The Supreme Court, which has a Chief Justice as its head and 14 Associate Justices, occupies the highest tier of the judiciary. The justices serve until the age of 70. The justices are appointed by the president on the recommendation of the Judicial and Bar Council of the Philippines.[3] The sitting Chief Justice is Lucas Bersamin,[4] the 25th to serve in that position.
Other court types of courts, of varying jurisdiction around the archipelago, are the:
Lower Collegiate Courts:
- Court of Appeals
- Court of Tax Appeals
- Sandiganbayan
Regular Courts:
- Regional Trial Courts
- Municipal Circuit Trial Courts
Muslim Courts
- Sharia District Courts
- Sharia Circuit Courts
Constitutional commissions[edit]
Article 9 of the Constitution of the Philippines establishes three constitutional commissions: the Civil Service Commission, the Commission on Elections, and the Commission on Audit.[5]
Office of the Ombudsman[edit]
See also: Corruption in the PhilippinesThe Philippine government or three of its branches are independently monitored by the office of the Ombudsman (Filipino: Tanodbayan). The Ombudsman is given the mandate to investigate and prosecute any government official allegedly guilty of crimes, especially Graft and Corruption. The Ombudsman is assisted by six deputies: the Overall Deputy, the Deputy for Luzon, the Deputy for Visayas, the Deputy for Mindanao, the Deputy for the Armed Forces, and the Special Prosecutor.
Local government[edit]
Main article: Administrative divisions of the Philippines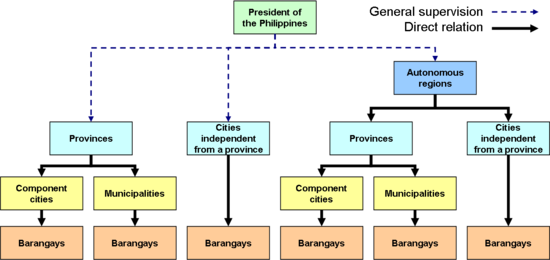 Local government hierarchy. The dashed lines emanating from the president means that the President only exercises general supervision on local government.
Local government hierarchy. The dashed lines emanating from the president means that the President only exercises general supervision on local government.The Philippines has four main classes of elected administrative divisions, often lumped together as local government units (LGUs). They are, from the highest to the lowest division:
- Autonomous regions
- Provinces (lalawigan, probinsiya, kapuoran) and independent cities (lungsod, siyudad/ciudad, dakbayan, dakbanwa, lakanbalen)
- Municipalities (bayan, balen, bungto, banwa) and component cities (lungsod, siyudad/ciudad, dakbayan, dakbanwa, lakanbalen)
- Barangays (also known as barrio)





